Van der Pol Oscillator
3. Van der Pol Oscillator
Parameter: $\mu$ (Damping coefficient)
Features
A nonlinear differential equation proposed by Dutch physicist Balthasar van der Pol to describe the behavior of vacuum tube circuits (triode oscillator circuits).
The most distinctive feature of this equation is that it possesses a specific trajectory where energy divergence and damping balance out, known as a "Limit Cycle". Regardless of the initial value, the system eventually gravitates towards this closed trajectory and maintains stable sustained oscillations.
When the parameter $\mu$ is large, the waveform deviates from a sine wave and becomes a waveform called "Relaxation Oscillation", characterized by repeated rapid charging and discharging.
Behavior of Solution (Phase Plane Plot)
Draws the trajectory on the phase plane with displacement $x$ on the horizontal axis and velocity $\dot{x}$ on the vertical axis.
By changing parameter $\mu$ with the slider, you can observe how the limit cycle shape transitions from circular (simple harmonic motion) to distorted (relaxation oscillation).
Fig 1: Trajectory in phase space. Whether starting from the outside or inside, it converges to the thick orbital line (limit cycle).
Results
The results of analyzing the Van der Pol oscillator using the trapezoidal method are shown below.
In this analysis, instead of direct programming, we performed the analysis using the "SPICE-Oriented Analysis Method," a methodology based on the reverse idea of describing the equation as a circuit and solving it with a circuit simulator (SPICE).
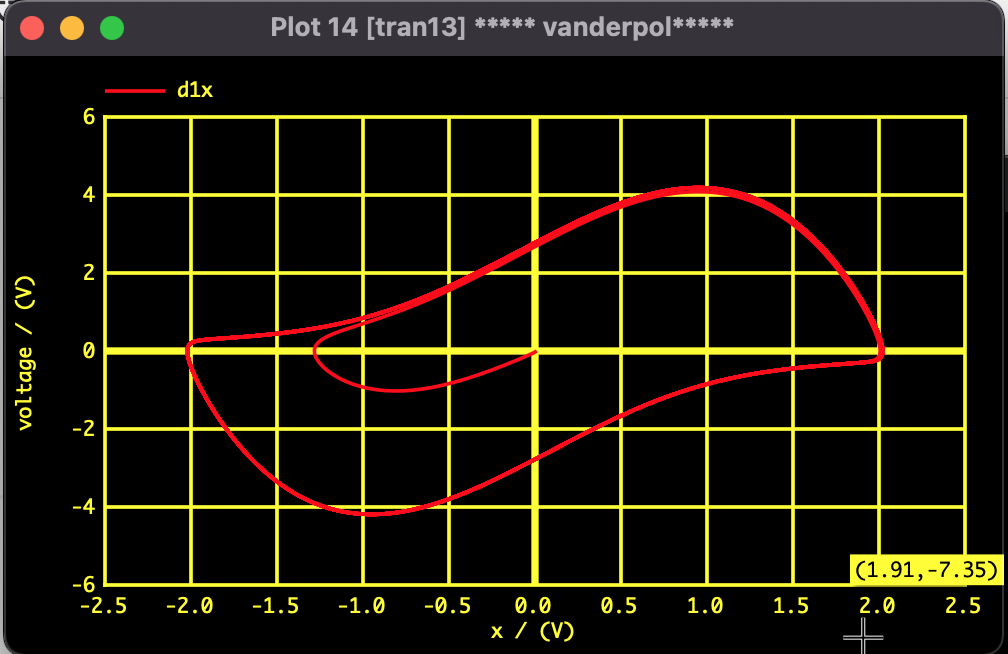
Fig 2: Waveform of Van der Pol Oscillator by SPICE-Oriented Analysis Method (Time Domain)
Analysis Environment
- SPICE: Mac SPICE3
- PC: MacBook
- OS: macOS Monterey 12.7.6
- CPU: 1.2GHz Dual-Core Intel Core m5
- Memory: 8GB
Since a calculation of this scale converges instantly in the current PC environment, detailed measurement of calculation time is omitted.